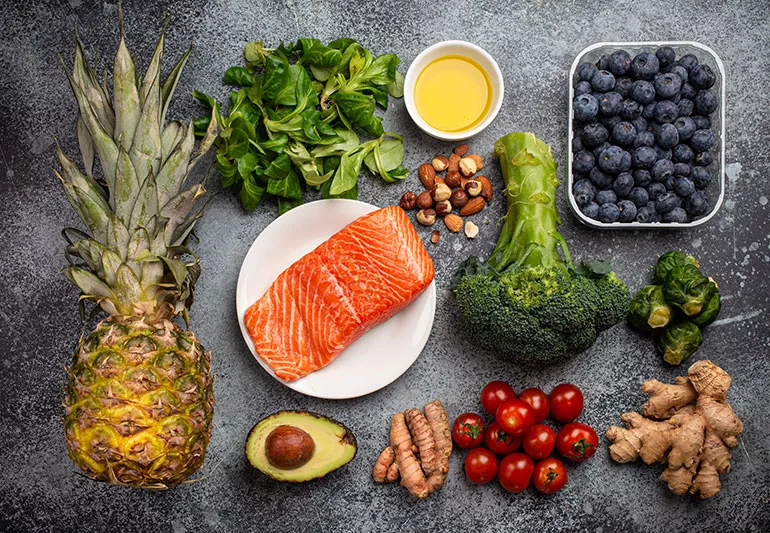
An anti-inflammatory diet focuses on foods that help reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is linked to various health conditions, including heart disease, arthritis, and certain types of cancer.1 By incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet, you can promote overall health and well-being.
Key Anti-Inflammatory Foods
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have powerful anti-inflammatory properties.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are packed with antioxidants that can help reduce inflammation.
- Leafy Green Vegetables: Spinach, kale, and collard greens are excellent sources of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and fiber.
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil: A healthy source of monounsaturated fats, which can help reduce inflammation.
- Turmeric: This golden spice contains curcumin, a potent anti-inflammatory compound.
- Garlic and Onions: These flavorful foods have anti-inflammatory properties and can boost immunity.
Tips for an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
- Limit Processed Foods: Processed foods often contain unhealthy fats, added sugars, and artificial additives that can contribute to inflammation.
- Reduce Red Meat Intake: Opt for lean protein sources like poultry, fish, and legumes.
- Minimize Sugar Intake: Excessive sugar consumption can lead to inflammation.
- Choose Whole Grains: Whole grains are rich in fiber and other nutrients that can help reduce inflammation.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your body hydrated and promote optimal health.
By incorporating these anti-inflammatory foods and lifestyle changes into your diet, you can reduce inflammation, improve your overall health, and enhance your quality of life.
Would you like to learn more about specific recipes, meal plans, or other tips for an anti-inflammatory diet?