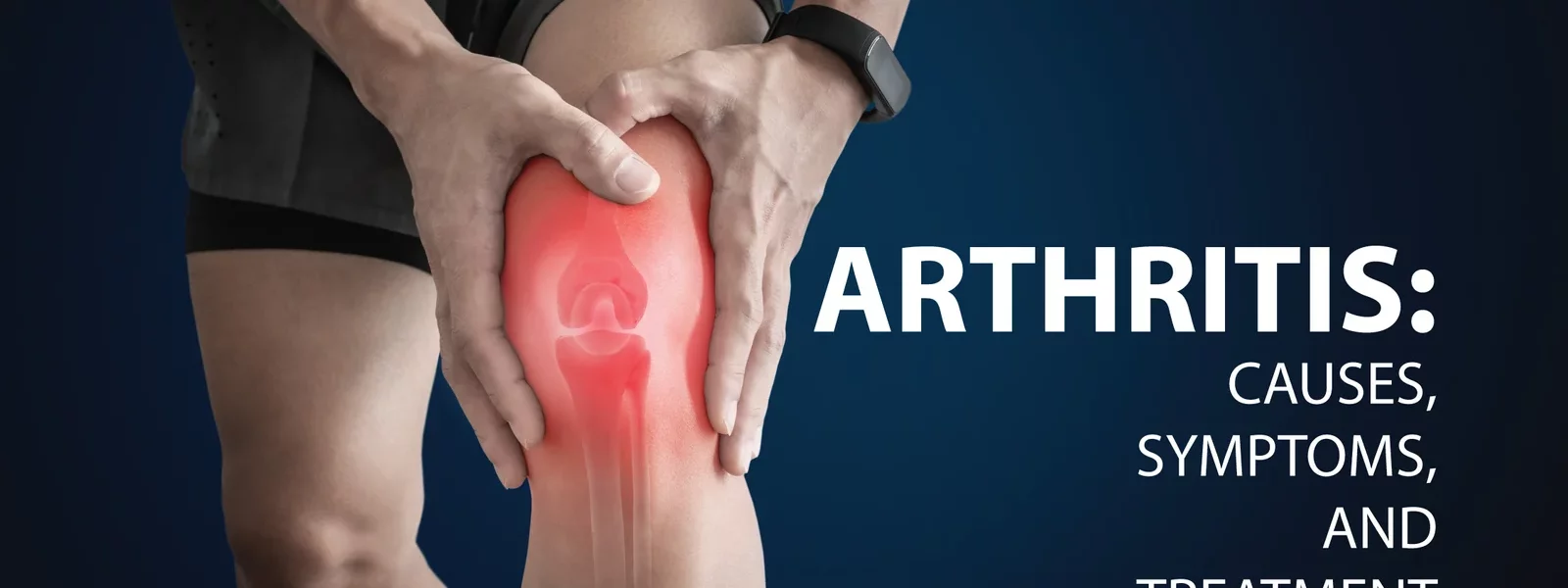
Arthritis is a general term for conditions that cause joint pain and inflammation. It affects millions of people worldwide, particularly as they age.
Types of Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis:
- Most common type, often associated with wear and tear on the joints.
- Cartilage breaks down, causing bones to rub together.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
- An autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints.
- The body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the joints.
- Gout:
- A type of arthritis that causes sudden, severe attacks of pain, especially in the big toe.
- High levels of uric acid in the blood lead to the formation of sharp crystals in the joints.
Symptoms of Arthritis
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Swelling
- Redness
- Decreased range of motion
- Fatigue
- Fever
Managing Arthritis
There’s no cure for arthritis, but treatments can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Medication: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve joint function, strength, and flexibility.
- Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy can help adapt daily activities to reduce joint stress.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on the joints.
- Low-Impact Exercise: Regular exercise, such as swimming or water aerobics, can help improve joint function and reduce pain.
- Assistive Devices: Canes, walkers, and braces can help support joints and improve mobility.
Lifestyle Changes
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can reduce inflammation.
- Regular Exercise: Low-impact exercises can improve joint health.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation and yoga can help reduce stress and inflammation.
- Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for overall health and can help manage pain.
By understanding arthritis and taking proactive steps to manage it, individuals can improve their quality of life and reduce the impact of the disease.